Real-time imaging:in case of atrial fibrillation



U.S. Department of
Health and Human
Services
National Institutesof Health
National Heart, Lung,and Blood Institute
Peter Kellman, Ph.D.

Disclosures
I have no financial relationships to disclose.
- and -
I will discuss the following off label use in my presentation:
Use of contrast agent for late enhancement imaging
Peter Kellman, Ph.D., NHLBI/NIH

144x256 matrix -> 1.9x1.4 mm2
8 HB breath-hold (incl. 1 discard)
(24.5 ms)
undersampling with net acceleration = 2.4
Beat
1
Beat
2
Beat
3
Beat
4
Beat
5
Beat
6
Beat
7
fully
sampled
reference
data
3x
under-
sampled
data
Segmented Breath-held AcquisitionTypical Protocol
beat 1
beat 2
beat 3

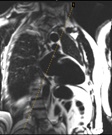
Subject with atrial fibrillation:breath-held segmented, retro-gated cine
144x256 matrix
1.9x1.4 mm2
24.5 ms
Parallel imaging factor 2.4
8 HB breath-hold
discard

Subject with atrial fibrillation:breath-held segmented, retro-gated cine
discard
144x256 matrix
1.9x1.4 mm2
24.5 ms
Parallel imaging factor 2.4
8 HB breath-hold

~ 17.4 frames
(57.5 ms)
uniform undersampling with acceleration = 4
92x192 matrix -> 2.9x1.9 mm2
4x
under-
sampled
data
Real-time Free Breathing AcquisitionTypical protocol with parallel imaging

Subject with atrial fibrillation:real-time free-breathing cine
parallel imaging factor 4
92x192 matrix
2.9x1.9 mm2
57.5 ms

Subject with atrial fibrillation:real-time free-breathing cine

Pseudo m-mode

~ 32 frames
(31.4 ms)
partial
Fourier
acquisition
“random” variable density undersampling with net acceleration = 9.4
120x192 matrix -> 2.3x1.9 mm2
Real-time Free Breathing AcquisitionCompressed sensing protocol
M Schmidt, O Ekinci, J Liu, A Lefebvre, MS Nadar, E Mueller, MO Zenge. “Novel highlyaccelerated real-time CINE-MRI …”. J Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2013,15(Suppl 1):P36. (based on SIEMENS CV_Sparse WIP implementation)

Subject with atrial fibrillation:real-time free-breathing cine
Sparse sampled, compressed sensing reconstruction
120x192 matrix
2.3x1.9 mm2
31.4 ms

Single heartbeat late enhancement
•Rapid, multi-slice acquisition
•Arrhythmia insensitive
•Free-breathing acquisition
Huber A, et al., Investigative Radiology. 2006 Feb;41(2):148-53.
Huber A, et al., AJR. 2006 Mar;186(3):627-33.
Sievers B, et al., Circulation. 2007 Jan 16;115(2):236-44.
inversion
imagereadout
Kellman P, et al., MRM. 2004 Feb;51(2):408-12.
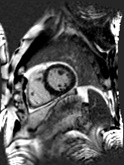
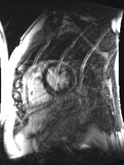
conventional
segmented with
poor breath-hold
single-shot
free breathing

Free breathing late enhancement
accelerated
single shotacquisition
respiratorymotioncorrection
averaging
raw
motion corrected
Full FOV
zoom
SENSE rate 2
Kellman P, et al., MRM. 2004 Feb;51(2):408-12.
Ledesma-Carbayo MJ, et al., JMRI. 2007. Jul; 26(1):184-190
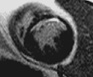
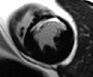

Conventionl
IR-turboFLASH
breath-held
accelerated single-shot
IR-trueFISP
free-breathing
single frame
16 HB
single frame
2 HB
8 averages
16 HB
motion
corrected
same acquisition time
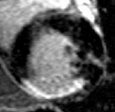
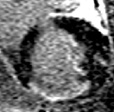
Respiratory Motion Corrected Averaging:
Selective averaging between 25-50% of “best”frames effectively mitigates thru plane motion

Rate 3 with 256x144 matrix
motion corrected
average
single heart beat
images
motion corrected

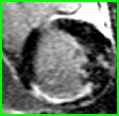
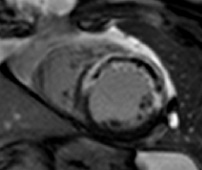
Subject in atrial fibrillationPSIR LGE
motion
corrected
average
single
heart beat
images
motion
corrected

Single-shot fat water separated imaging
motion
corrected
average
single
heart beat
images
motion
corrected
water
fat
1 2 3 M
N-echoes per PE line
Single shot, Rate = 3 parallel imaging
(multiple repetitions)

Single-shot fat water separated imaging
motion
corrected
average
single
heart beat
images
motion
corrected
water
fat

Review
Review
•Free-breathing real-time cine function
•parallel imaging
•compressed sensing
•Free-breathing PSIR LGE
•accelerated, single shot
•respiratory motion corrected
•selective averaging
•Free-breathing Fat water separated imaging
•Dark blood prepared or PSIR LGE
•Fusion of images with ECG signals