Application of Fat/Water SeparatedImaging in the Heart
Water
Fat



U.S. Department of
Health and Human
Sevices
National Institutesof Health
National Heart, Lung,and Blood Institute
Peter Kellman, Ph.D.

Disclosures
I have no financial relationships to disclose.
- and -
I will discuss the following off label use in my presentation:
Use of contrast agent for late enhancement imaging
Peter Kellman, Ph.D., NHLBI/NIH

Motivation:Tissue characterization
•Intramyocardial fat
•Fibro-fatty infiltration
•Epicardial, Pericardial, & Visceral Fat
•Tumors/masses (lipomas)

Motivation:Artifact mitigation
•Bright fat signal elimination
•Chemical shift
•Out-of-phase cancellation (partial volume)
•Short T1 apparent “late enhancement”

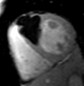
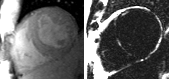
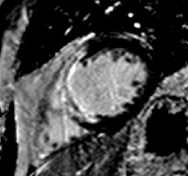
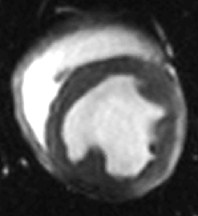
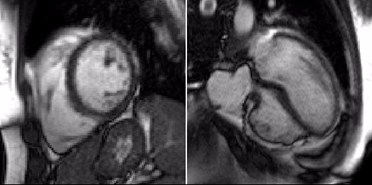
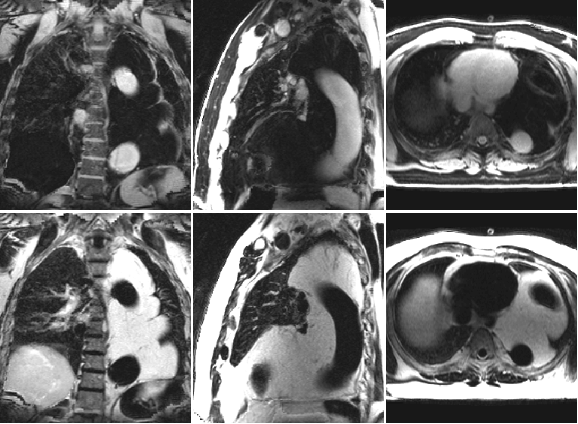
Fat in and around the heart:
WATER
intraatrialseptum
epicardial
fat
mediastinal
fat
parietal
pericardium
FAT
interventricularseptum
coronary
lumen
AV groove
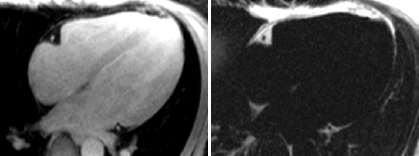
coronary lumen
(bright blood)
(dark blood)

Sequence variations:
Cine
Bright blood
Dark blood prep
PSIR-GRE
late enhancement
Single-shot
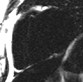

Sequence:multi-echo GRE (single phase)
Typical parameters:
acquisition: ECG triggered (1 R-R), segmented
matrix size:256x144
readout flip angle:12 degrees
number of echoes:4 (monopolar readout)
bandwidth:977 Hz/pixel
TE (TR):1.6, 4.2, 6.7, 9.2 ms (11.2 ms)
views-per-segment:19 (8 heartbeats + 1 discarded)
1 2 3 M
N-echoes per PE line
Optional IR or DB prep

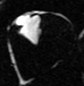
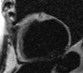
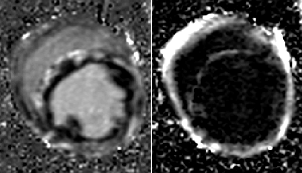
Tissue Characterization:
Fibro-fatty infiltration1:Potential arrhythmogenic substrate
1Burke AP, et al. Arrhythmogenic RV Cardiomyopathy and Fatty Replacement of the RightVentricular Myocardium: Are They Different Diseases? Circulation. 1998 Apr 28;97:1571-80.
2Bluemke DA, et al. MR Imaging of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy:Morphologic Findings and Interobserver Reliability. Cardiology. 2003;99:153-62.
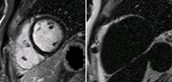
Water
Fat
suppressed
Water
Fat
Current limitation:
Subjective interpretation2

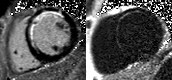
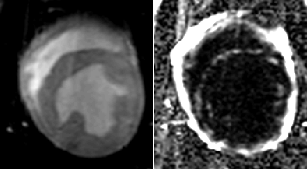
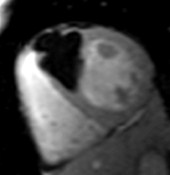
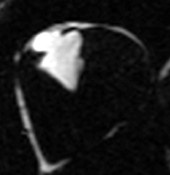
Patient with myocardial lipodystrophy
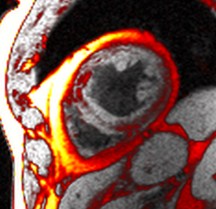
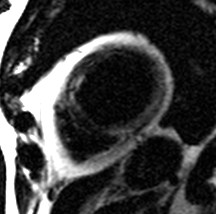
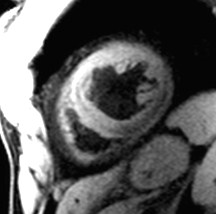
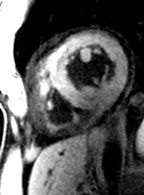
water
fat
combined
water + fat
Fat-water separation
•Positive contrast
•Improved sensitivity
•Independent of shim
•Objective interpretation

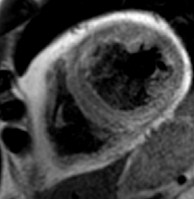
Extensive fatty infiltration in themyocardium
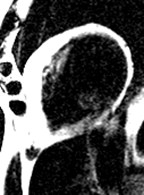
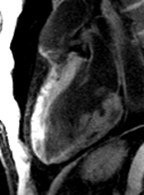
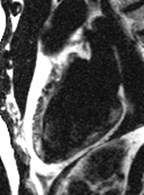
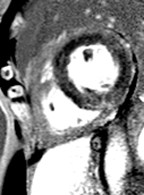
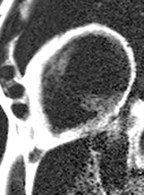
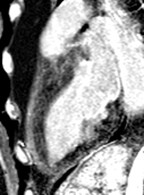
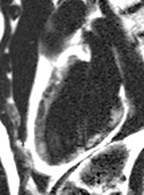
WATER
FAT
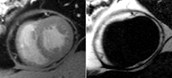
Pre-contrast
Late enhancement
WATER
FAT

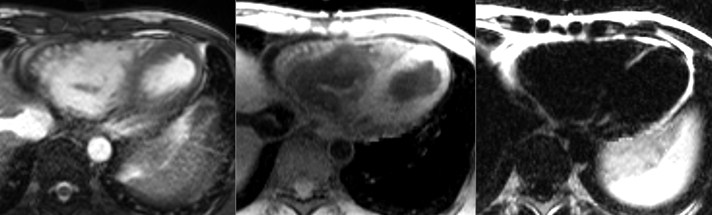
37-year-old male who presented with exertional ventricular tachycardia and a familyhistory of unexplained sudden death in his mother in her 30’s
The overall clinical presentation and findings are consistent with the diagnosis ofarrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
Water
Fat
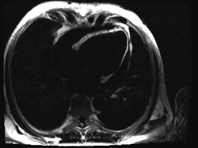
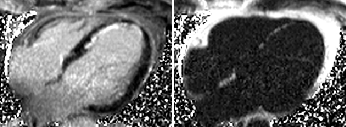
SSFP cine still frame
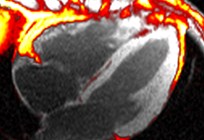
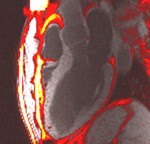
thin finger-like projections of fatinto the right ventricular free wall
Fat in moderator band
Fat in septum

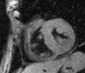
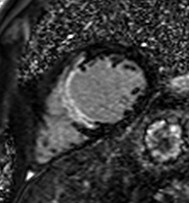
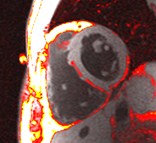
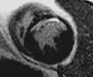
Chronic MI Patient:Fibro-fatty infiltration
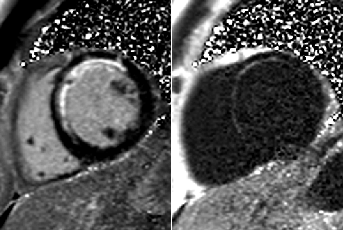
Fatty
infiltration
MI

TSE FAT sat
TSE
Water
Fat
conventional
chemical shift
fat-saturation
multi-echo
water-fat
separation


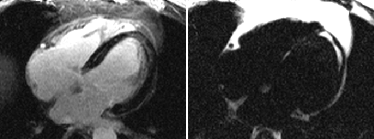
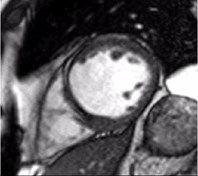
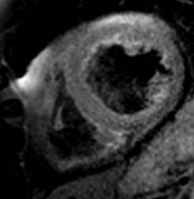
Intramyocardial Fat:may lead to false late enhancement
WATER
FAT
conventional PSIR
late enhancement
multi-echo PSIR
fat/water separated
late enhancement
apparent lateenhancement
inversion time(TI)
magnetization
normal
MI
fat


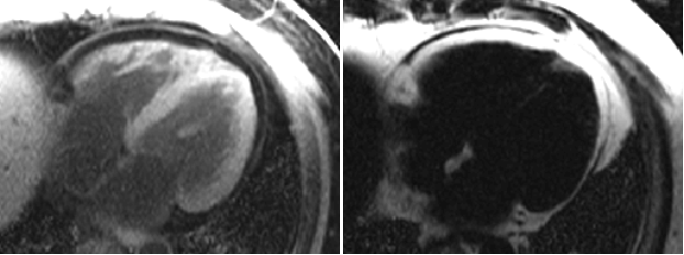
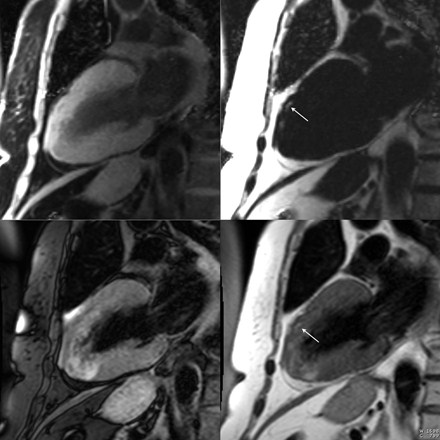
Patient with nonischemiccardiomyopathy

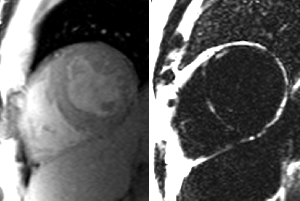
WATER
FAT
WATER
FAT
Pre-contrast
Late enhancement
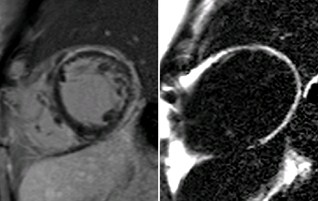
Patient with nonischemiccardiomyopathy

Patient with nonischemic cardiomyopathy
sub-epicardial late enhancement
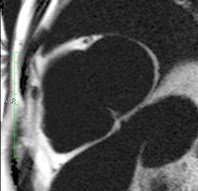
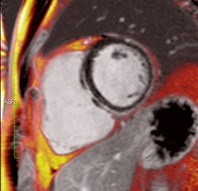
Conventional PSIR
PSIR Water
PSIR Fat
Water + Fat

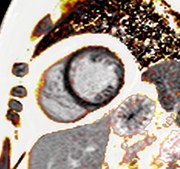
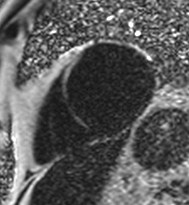
Patient with fat infiltrating trabeculae
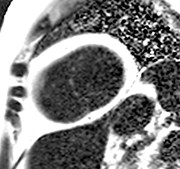
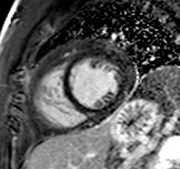


Improved visualization andmeasurement of parietal pericardium
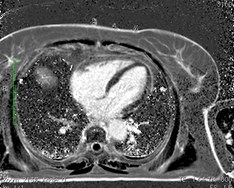
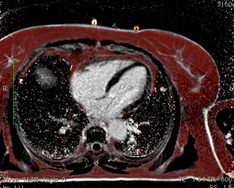
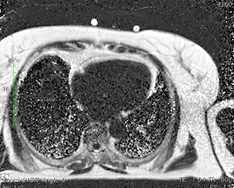
Water
Fat
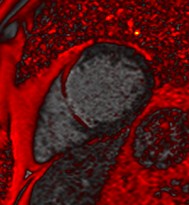
Fat (red) fused with water
Water (red) fused with fat

Improved visualization andmeasurement of parietal pericardium
Water
Fat
Water (red) fused with fat
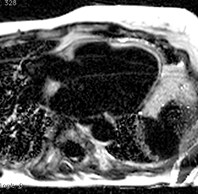
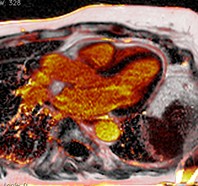
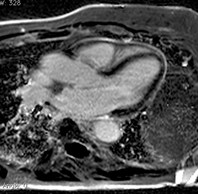

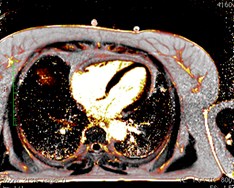
Patient with constrictive pericarditis
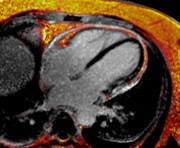
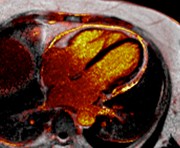
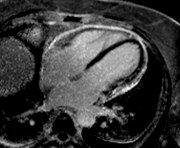
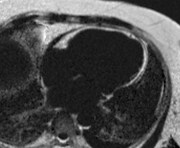
Conventional
PSIR LGE
PSIR Water
PSIR Fat
Water + Fat
Water + Fat

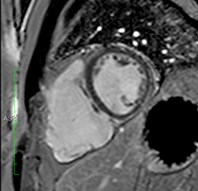
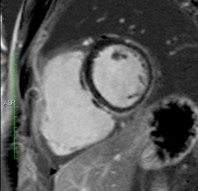
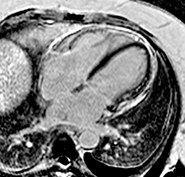
A 48-year-old female underwentpreoperative stress nuclear imaginga fixed anteroseptal defect was revealed which wasreported as consistent with myocardial infarction

CMR demonstrated an intramyocardial lipomawithin the anteroseptumcorresponding to the fixed defect seen by nuclear techniques
Conventional
chemical shift
fat-saturation
method
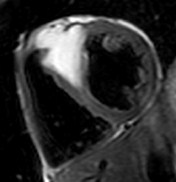
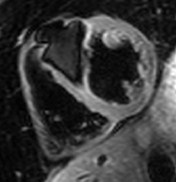
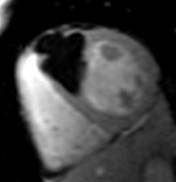
TSE FAT sat
TSE
Water
Fat
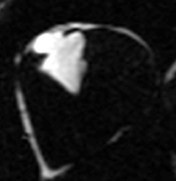
Multi-echo Dixon
water-fat separation

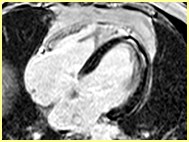
Intramyocardial lipomaFat water separated cine

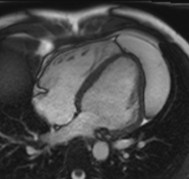
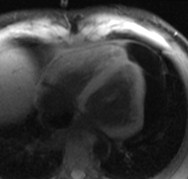
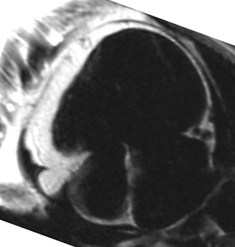
SSFP cine(still frame)
Water
Fat
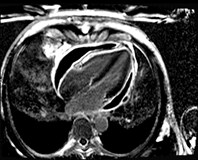
Patient with interpericardial lipoma

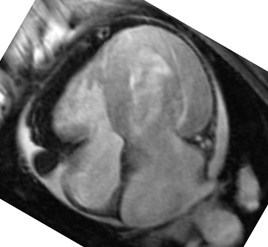
Water
Fat
Echo
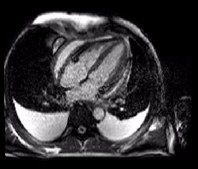
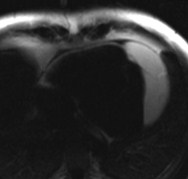
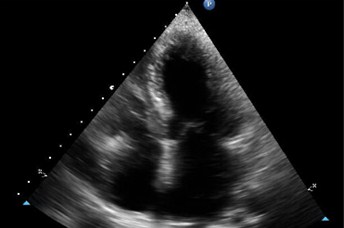
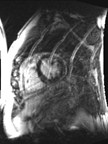
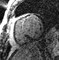
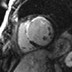
Patient with suspected intracardiac mass by echo
found to have prominent epicardial fat with lobulation adjacent to rightatrioventricular groove.

Patient referred by Echo to characterize mass
significant mass of fat attached to RV free wall

Patient with aortic dissection and prior omentoplasty
Significant fat within the left hemithorax

Single shot acquisition
accelerated
single shotacquisition
respiratorymotioncorrection
averaging
•Rapid, multi-slice acquisition
•Arrhythmia insensitive
•Free-breathing acquisition
conventional
segmented with
poor breath-hold
single-shot
free breathing

Sequence:single shot, multi-echo GRE
Typical parameters:
acquisition: ECG triggered (1 R-R)
matrix size:192x108 (36 PE lines acquired)
readout flip angle:20 degrees
number of echoes:2 (monopolar readout)
bandwidth:965 Hz/pixel
TE (TR):2.38, 4.76 ms (5.9 ms)
# repetitions:8
1 2 3 M
N-echoes per PE line
Single shot, Rate = 3 parallel imaging
(multiple repetitions)

Late enhancement sequence:single shot, multi-echo PSIR GRE
Typical parameters:
acquisition: ECG triggered (2 R-R), single shot
matrix size:192x108 (36 PE lines acquired)
readout flip angle:25 degrees
number of echoes:2 (monopolar readout)
bandwidth:965 Hz/pixel
TE (TR):2.38, 4.76 ms (5.9 ms)
# repetitions:8 (16 heartbeats)
1 2 3 M
N-echoes per PE line
IR data
(25° flip angle)
reference data
(5° flip angle)

Motion correction
apply
motioncorrection
averaging
fat-water
separated
image recon
non-rigid
image
registration
apply
motioncorrection
+
averaging
water
fat
motion field

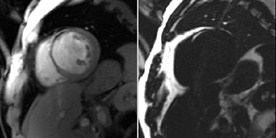
Chronic MI with Fibro-fatty infiltration:Pre-contrast Fat/Water separation
WATER
FAT
Raw images
(8 repetitions)
Motion corrected
Motion corrected average

Chronic MI with Fibro-fatty infiltration:PSIR Late Enhancement with Fat/Water separation
WATER
FAT
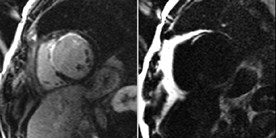
Raw images
(8 repetitions)
Motion corrected
Motion corrected average

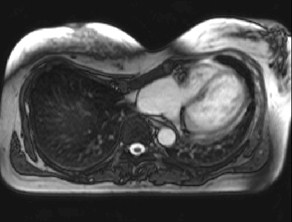
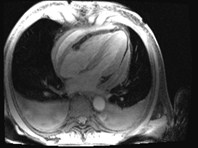
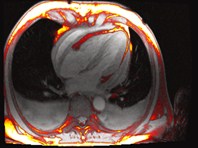
RV appearance had severeinvagination of right AV groove“pinching” the tricuspid annulus
“caved-in” chest wall deformity
resulting in a leftward shift of herheart and vascular structuresfrom midline
Axial localizer
SSFP cines
Patient with pectus excavatum
Required 3D volumetric acquisition in order to orient eachventricle in isolation and measure true annular diameters
Required water fat suppression to assess possibility of fattyreplacement of RV myocardium

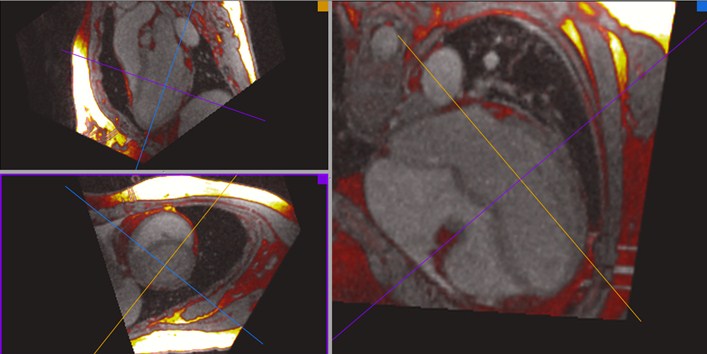
Volumetric 3D GRE Fat-Water acquisition:
Assessment of RV
Navigated 3D (6.5 min acquisition)
1.5 mm^3 true (non-interpolated) isotropic resolution (160x160x144)
Axial slab, 2D acceleration, rate 4x2 = 8
GRE 3 echoes

Benefits of water-fat separation
•fat has positive contrast
•more objective
•positive correlation of fatty infiltration &fibrosis using fat-water late enhancement
•robust in the presence of backgroundfield variation
•uniform fat suppression (water image)
•water and fat images acquired in a singlebreath-hold
•decreased fat related artifacts